

| シリコーンとは | 環境・安全 | よくある質問と回答 |

シリコーンは、その優れた特性により多くの産業分野で広く使用されています(シリコーンの用途)。 特に、その安全性に対する評価を得て、食品添加物、食品用器具類、化粧品、医薬器具等への使用も必要な認可を得て、幅広く応用されています。
これまでの多くの科学的研究結果に基づき、シリコーンは意図した用途に使用される限り、ヒト健康と環境に対して安全であると我々は確信しています。シリコーン工業会は、ヒト健康、野生生物や自然環境の保護を優先します。シリコーン工業会は、今後も継続的にシリコーン製品の環境・安全性を検証し、その結果を規制当局と共有します。
ジメチルポリシロキサン環状シロキサン
環境中でのシロキサン
健康・安全に対する取り組み
工程安全ガイドライン
シリコーン製品の中で、最も長い間、また最も大量に生産、使用されてきた代表的なポリジメチルシロキサン(粘度10cSt以上)の環境・安全性について説明します。
ポリジメチルシロキサンは、安全性の見地からの検討や試験が世界中で豊富に行われてきました。たとえばポリジメチルシロキサンのLD50値は、他の化学物質と比較して大きな数字であり、急性毒性が極めて低いことを示しています。さらに様々な角度からの安全性評価が行われてきており、総合的に安全性の高い物質であることが確認されています。
環境に排出される少量のポリジメチルシロキサンの大部分は、活性汚泥の廃棄により、土壌環境に堆積します。ポリジメチルシロキサン環境濃度を陸生生物、水生生物について測定された無影響濃度と比較すると、ポリジメチルシロキサンは環境に対する悪影響を及ぼすとは予想されません。
環状シロキサンとは、ケイ素原子上に2つのメチル基を持つケイ素原子(Si)が酸素(O)原子と結合したジメチルシロキサン単位 (CH3)2Si-O-を有する環状構造をもったシロキサンで、シリコーン製品の製造原料として使われています。中でも環状シロキサンとして一般的なものがD4、D5およびD6です。
D4として一般的に知られているオクタメチルシクロテトラシロキサンは、ジメチルシロキサン単位 (CH3)2Si-O-を4つ有する環状構造をもったシロキサンです。
D4は、無色透明の液体で、シリコーンゴム、シリコーンゲル、シリコーンオイルなどを製造する中間体として主に使用されます。
製造されたD4の大部分はシリコーンメーカーにて中間体として消費されます。その一部はシリコーンメーカーから顧客へ出荷され、他の有機材料をシロキサンで変性するための工業原料として使用されます。
D4の「健康と環境」に関するより詳細な情報については
http://www.cyclosiloxanes.org/D4_health_environment_properties
をご覧ください。
D5として一般的に知られているデカメチルシクロペンタシロキサンは、ジメチルシロキサン単位 (CH3)2Si-O-を5つ有する環状構造をもったシロキサンです。
D5は、無色透明の液体で、シリコーンゴム、シリコーンゲル、シリコーンオイルなどを製造する中間体として主に使用されます。
製造されたD5はシリコーンメーカーにて中間体として消費され、一部はスキンクリームやデオドラントなどの化粧品の原料成分として使われます。それが配合された化粧品には「シクロメチコン」または「シクロペンタシロキサン」と成分表示されています。
D5はパークロロエチレン代替としてドライクリーニング溶媒としても使用され、労働者、消費者および環境に対するパークロロエチレンへの暴露削減に寄与しています。
D5の「健康と環境」に関するより詳細な情報については
http://www.cyclosiloxanes.org/D5_health_environment_properties
をご覧ください。
D6として一般的に知られているドデカメチルシクロヘキサシロキサンは、ジメチルシロキサン単位 (CH3)2Si-O-を6つ有する環状構造をもったシロキサンです。
D6は、無色透明の液体で、シリコーンゴム、シリコーンゲル、シリコーンオイルなどを製造する中間体として主に使用されます。
製造されたD6はシリコーンメーカーにて中間体として消費され、一部はスキンクリームやデオドラントなどの化粧品の原料成分として使われます。それが配合された化粧品には「シクロメチコン」または「シクロヘキサシロキサン」と成分表示されています。
D6の「健康と環境」に関するより詳細な情報については
http://www.cyclosiloxanes.org/D6_health_environment_properties
をご覧ください。
D4、D5、D6は無色透明の液体です。以下にそれらの主要な物理化学性質を示します。
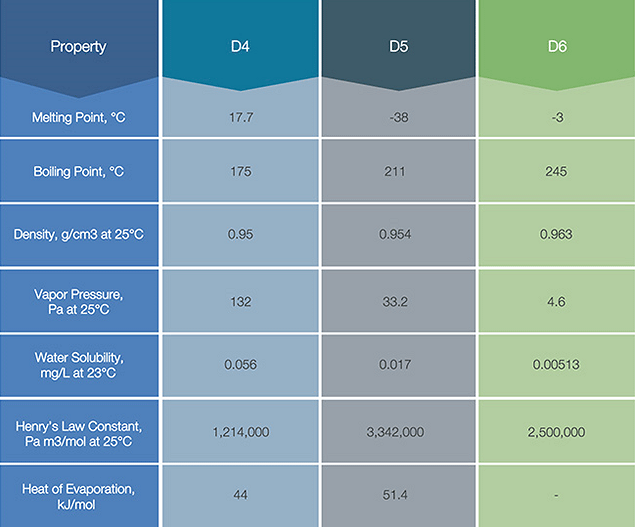
D4、D5、D6は水への溶解度が低く、高いヘンリー定数を持ちます。このことはD4、D5、D6が容易に大気中に揮発することを意味します。
シリコーンは様々な製品に利用され、現代生活の質の向上、安全性の向上、省エネルギーなどに役立っています。しかし、これらの利点も環境を犠牲にして成立つのでは意味がありません。
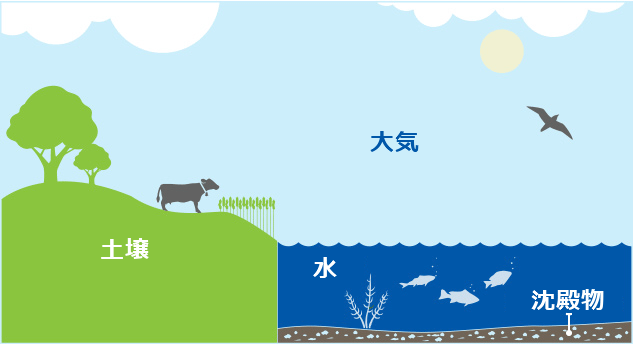
環境中で検出されるシロキサンとして、主にD4、D5、D6などの揮発性シロキサン(VMS)および揮発性の低いシロキサン(PDMS)があります。
以下の図は、水、堆積物、土壌、および大気中でのこれらシロキサンがどのように挙動するかをまとめたものです。詳細については以下の図のそれぞれの場所をクリックしてください。
グローバルで活動する私どもシリコーンメーカーにとって野生生物や自然環境を保護することは重要な責務です。私たちは工業会として過去35年以上にわたり労働者、消費者、環境および製造プロセスに関わるシリコーンの安全性を評価するための科学的研究を行っています。
具体的には、コンピュータモデリング、実験室試験、環境モニタリングおよび最新の科学的手法を用いたシロキサンの科学的研究やリスク評価を行っています。これらの研究データを日本や海外の規制当局に共有しています。
このような活動を通じ、本来の目的用途に使用される限りにおいて、私どもが提供する製品は安全であると確信しています。
環状シロキサンに関連する研究や有用なリンクについては、「新着情報」セクション
http://www.cyclosiloxanes.org/news_studies_cyclosiloxanes_D4_D5_D6
にアクセスするか、D4とD5のよくある質問
http://www.cyclosiloxanes.org/links/23/38/FAQ-D4-D5-Europe-North-America-and-Japan
をご覧ください。
他の多くの製品と同様に、最終製品を製造するために使用するシリコーン中間体も、その製造作業、保管、輸送などにつき、安全を確保するため適切に取り扱う必要があります。
下記のシリコーン原料につき、シリコーン工業会が提供する安全ガイドラインを理解頂き、適切に取り扱い下さる様お願いします。
|
Copyright © 2001 - SIAJ, All Rights Reserved. |